How agile MDM enables faster time to insights for life sciences
Reading Time: 5 minutes

Data is the lifeblood of success in the life sciences industry. From groundbreaking drug discovery to personalized patient care, effective data utilization fuels innovation across the board. However, a study by McKinsey1 revealed that siloed data sources as the biggest hurdle to adopting digital and analytics within the organization.
Many organizations may lack a clear understanding of their own data assets, as enterprise data is often dispersed across various systems, making access and discovery challenging. Data available in inconsistent formats may not be fit for use, while fragmented, poor quality of data can lead to remediation, process delays, efficiency and even lead to customer churn. According to Gartner, poor data quality can cost an average of $15 million to organizations annually.
Role of Master Data Management (MDM)
A HFS Horizons Report2 states that up to 30% of life sciences enterprise leaders are struggling to meet their strategic objectives due to poor automation of data and processes. Inefficiencies in data can impact the speed and effectiveness of commercial decisions.
This underscores the need for a comprehensive data management and integration mechanism that can be achieved by Master Data Management (MDM). MDM involves maintaining a unified, trusted, real-time and interoperable source of reference data for various data users within an organization.
MDM is crucial in the life sciences industry for several reasons:
- High regulation requires compliance with data privacy, security, and clinical trial regulations
- Data-intensive nature of the industry necessitates vast amounts of patient, product, and clinical trial data being collected and stored
- Rapid evolution of new technologies and industry dynamics
MDM helps organizations to meet regulatory requirements by ensuring quality and consistent data in a cost-effective manner. MDM helps organizations adapt and operate effectively amidst a changing industry landscape.
Common challenges to data management
The growing volume, variety, and veracity of data in clinical research have led to greater complexity in data management. The life sciences and biopharma industry faces some challenges in maintaining and managing data, such as:
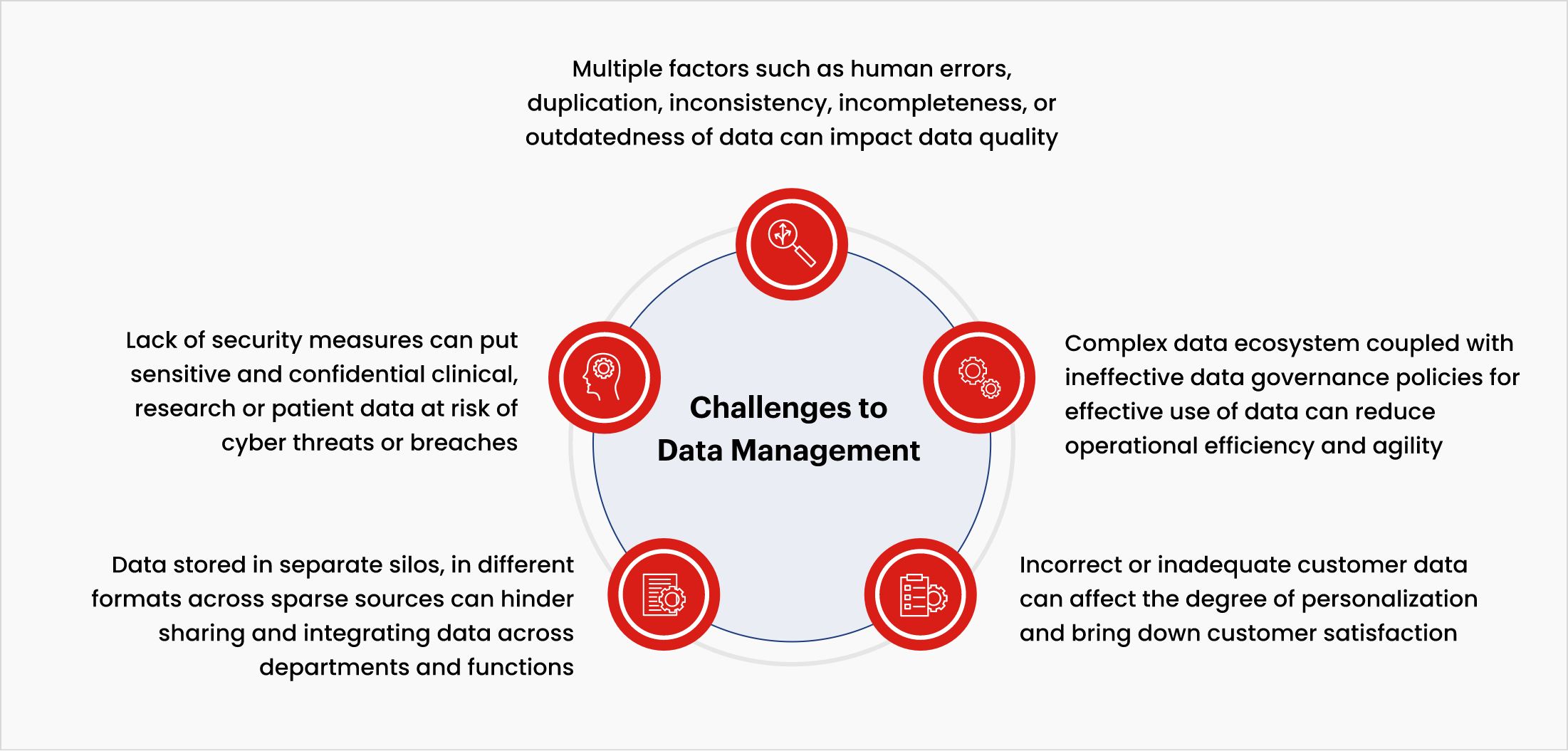
MDM– A key enabler for making businesses data-driven
A multi-domain MDM platform can drive consumer insights, revenue increase, productivity boost, and lower cost of sales. Other benefits include:
- Creating a shared and trusted single view of customer data for marketing, sales, and service purposes
- Improving lead times for launching new products
- Synchronizing product and location data across the supply chain
- Streamlining business operations and process workflows to enhance decision-making effectiveness
- Achieving higher operational efficiency to control costs
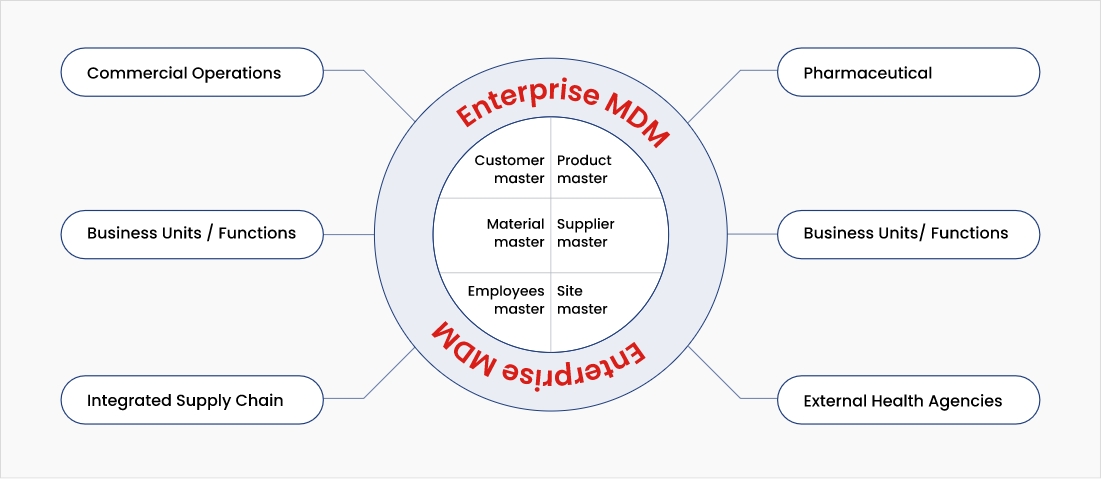
Organizations that adopt a multi-domain MDM platform with data governance practices can realize immense value across the following use cases:
Patient-centered supply chain
MDM integrates data across R&D stages helps to uncover insights from trial-data and real-world evidence that can be used to predict formulations for drug discovery.
Accelerated drug discovery
MDM integrates data across R&D stages helps to uncover insights from trial-data and real-world evidence for predicting formulations for drug discovery faster than before.
Effective commercial analytics
MDM helps to maintain a single source of truth for improving time to insights. This drives better sales ops, marketing, financial and commercial strategy.
Improved sales performance
Connected and complete HCP/HCO data enables sales reps to deliver better physician experiences across channels. MDM can facilitate accurate sales reporting for compensation management.
Data integration
MDM integrates diverse data sources, over a single source of truth with accurate, up-to-date information that fosters collaboration and enables seamless data sharing across stakeholders.
Data governance
Governance mechanisms implemented through MDM ensure that enterprise data is always compliant to various regulations so that the privacy, security, and integrity of health information is assured.
Entity resolution
Flexible match-and-merge capabilities in MDM can deduplicate data entries, improves data connectivity, eliminates errors and ensures standardization. Data lineage helps to track relationships and patterns within the data for effective decision-making.
Data enrichment
MDM enables extraction of data from legacy systems, simplifies enrichment with external data and supports centralized search for faster insights. Well managed data can support digital platforms and analytics solutions with real-time, trusted data.
Essentials for building a multi-domain MDM platform
Life science companies need to have a full-spectrum MDM platform to meet all data needs. A multi-domain approach, with a user-friendly interface, facilitates access to crucial information throughout the innovation lifecycle, promoting transparency and accountability. It must include the following elements for successful implementation:
- An integrated data infrastructure, comprising storage, integration tools, and analytics platforms, delivers data to stakeholders cost-effectively. Implementing approaches like DataOps, MLOps, and AI/ML streamlines data management processes for seamless operations.
- A robust data governance framework, supported by tools, ensures secure data access and usage. Investing in master data management and data quality is essential to maintain data integrity. Generative AI aids in creating security policies and rules for data handling.
- Data quality management practices support effective decision-making across business processes, including detection, prevention, and enhancement. Augmented MDM accepts data from various sources and improves quality over time through automation.
- Change management is crucial for MDM-driven transformations, involving process re-engineering, user interfaces, applications, documents, and skill development. Preparing for change management also means building the capability to adopt the latest techniques and technologies over time to keep up with the growing data complexity.
- MDM as an ongoing initiative includes continuous monitoring and improving data quality, governance, and processes to ensure it remains effective over time—update for data security and privacy to stay up to date with the changing industry landscape.
Conclusion
Today, the life sciences and pharmaceutical sectors rely significantly more on data. Establishing a single, accurate, and consistent source of critical information can enhance data quality, operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, decision-making, and collaboration within organizations. Modern, augmented MDM systems have accelerated the process of integrating data, such that a successful use case can be delivered in as little as six weeks. These systems are tailored to integrate digital and analytics capabilities to support innovation across the life sciences value chain.
References:
Featured blogs
Subscribe to get latest insights
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI
Featured blogs
Talk to our experts
Get the best ROI with Sigmoid’s services in data engineering and AI






